- Euro (€)
- Bulgarian Lev (BGN )
- Czeck Koruna (CZK )
- Hungarian Forint (HUF )
- Polish Złoty (PLN )
- Swedish krona (SEK )
- Swiss Franc (CHF )
- Canadian Dollar (CAD )
- Mexican Peso (MXN )
- Norwegian Krone (NOK )
- Chinese Yuan (CNY )
- Indian Rupee (INR )
- Australian Dollar (AUD )
- New Zealand Dollar (NZD )
- Saudi Riyal (SAR )
- UAR Dirham (AED )
- US Dollars (USD )
- GB Pound (GBP )
- Danish Koruna (DKK )
- Romanian Leu (RON )
-
 CatalogTop All products in one place
CatalogTop All products in one place
-
 Software Defined RadioPopular Explore Signals Beyond Limits
Software Defined RadioPopular Explore Signals Beyond Limits
-
 RFID/NFC Unlock Possibilities with RFID/NFC
RFID/NFC Unlock Possibilities with RFID/NFC
-
 Antennas Antennas for every signal need
Antennas Antennas for every signal need
-
 Amplifiers Signal Boosters & LNAs
Amplifiers Signal Boosters & LNAs
-
 Radio Communication Radio Communication Essentials
Radio Communication Radio Communication Essentials
-
 Test & Measurement Unleash Precision. Reveal Signals.
Test & Measurement Unleash Precision. Reveal Signals.
-
 FPGA DevelopmentNew Accelerate Ideas. Build Hardware.
FPGA DevelopmentNew Accelerate Ideas. Build Hardware.
Build Your Own Cheap ADS-B Radar with an RTL-SDR: A Comprehensive Guide
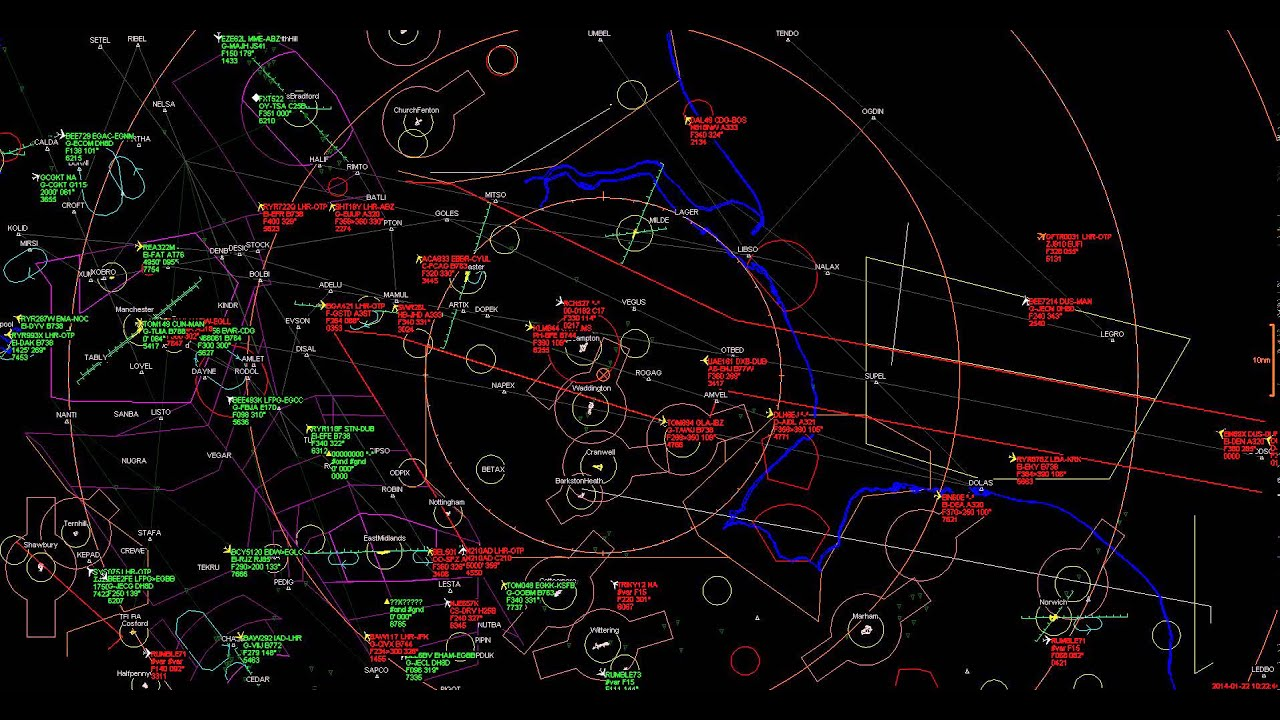
Have you ever looked up at the sky and wondered what kind of air traffic is zipping overhead? With a surprisingly affordable setup, you can turn your curiosity into reality! This guide will show you how to use an RTL-SDR (Software Defined Radio) dongle and free software to create your very own ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) aircraft radar system.
Why RTL-SDR?
Traditional ADS-B receivers can be quite expensive. But the RTL-SDR, a popular software-defined radio peripheral, can be purchased for as low as $20! It acts as a powerful receiver, picking up the ADS-B signals transmitted by airplanes, which include information like their position and altitude.
Software Stack:
To decode these signals and visualize them on a map, we'll be using two free and open-source programs:
- dump1090: This program acts as the workhorse, receiving the raw ADS-B data from the RTL-SDR and decoding it into a usable format.
- Virtual Radar Server (VRS): This software takes the decoded data from dump1090 and displays it on a user-friendly map interface, allowing you to see airplanes in real-time.
Here's what you'll need:
- RTL-SDR v3 or later: The most recent versions offer better performance.
- Antenna: This is crucial for good reception. Here's where things get interesting:
- If you purchased an RTL-SDR kit that includes a dipole antenna: Great news! You can actually use the included small whip antennas for receiving aircraft signals. While not ideal for long-range reception, they're a good starting point for picking up nearby air traffic.
- For improved range and performance: Consider investing in a dedicated ADS-B antenna designed for the 1090 MHz frequency. These antennas are typically dipole or directional designs and offer better signal strength compared to the small whip antennas.
- Computer: Any computer capable of running the software will suffice.
- Download and install:
- Download and install the latest version of dump1090 (https://github.com/MalcolmRobb/dump1090) To download for Windows simply go to the Git repository and download the dump1090 zip file.
- Download and install Virtual Radar Server (https://www.virtualradarserver.co.uk/Download.aspx).
Setting Up dump1090:
- Extract the downloaded dump1090 archive.
- Open a command prompt and navigate to the extracted folder.
- Run the command
./dump1090(Linux/Mac) ordump1090.exe(Windows). If prompted, allow firewall access for the program.
Configuring Virtual Radar Server (VRS):
- Open Virtual Radar Server.
- Go to the "Tools" menu and select "Options."
- Click on the "Receiver" tab and click "Wizard" and select "A software defined radio" press next and select "Dump1090" adn finish the wizard.
- Make sure Dump1090 is running on the specified port and click "OK."
- Click the blue link named
<b>127.0.0.1/VirtualRadar</b>to view the real-time aircraft traffic!
Additional Tips:
- Consult the dump1090 documentation for more advanced configuration options. You can fine-tune settings like gain and adjust filters to optimize reception.
- A good quality antenna with a clear view of the sky will significantly improve reception range. Especially if you're using the included small whip antenna, try placing it in a high and unobstructed location.
- Several online communities and forums dedicated to RTL-SDR users offer support and troubleshooting tips. A quick web search will point you in the right direction!
From Budget-Friendly to Feature-Rich:
This basic setup provides a fantastic introduction to the world of ADS-B aircraft tracking. As you delve deeper, you can explore advanced features offered by dump1090 and VRS, or even integrate your system with flight tracking websites.
So, fire up your RTL-SDR, whether you're using the included small antenna or have invested in a dedicated ADS-B antenna, and get ready to be amazed by the constant stream of air traffic buzzing across the skies above you!
We support all major card and digital payment options. More local methods are available and shown during checkout.
You enter into a binding sales contract once you have received an 'order confirmation and sales receipt' email from us, in line with our Sales & Delivery conditions. Therefore, sdrstore.eu has the right to cancel your order in the event of technical problems, delivery failure, Fair use policy and other similar situations.
© 2023 - 2025 SDRstore.
